The demand
The frequency and impact of disasters continues to rise, calling for effective disaster risk management and innovative risk financing solutions.
Disaster Risk Financing (DRF) can increase the ability of national and local governments, homeowners, businesses, agricultural producers, and low-income populations to respond more quickly and resiliently to disasters by strengthening public financial management and promoting market-based disaster risk financing.
However, although the frequency and severity of economic and insured losses caused by, for example, inland flood events have been increasing, the usage of DRF products for flood events is not yet extensive. The main reason for this is that capturing the appropriate triggers and physical properties of a flood event, such as its extent, depth, number of people affected, and/or the affected exposure, is challenging.
Recent improvements in quality and availability of satellite-derived characteristics increased the usability of EO products, allowing for better results and further synergies between actors, potentially expanding the market of Disaster Risk Financing applications.
The project e-Drift (Disaster risk financing and transfer) is financed by ESA and led by CIMA Research Foundation (IT) in the framework of the EO science for society programme through the action line dedicated to enabling business sector initiatives. The project has the aim to improve the performance of the EO products and provide an automated and reproducible way to support risk transfer and insurance. The purpose is to develop and verify innovative analytic capabilities exploiting new ICT, such as, for instance, cloud based processing, supply chain automation, etc. to provide the necessary support capabilities required by industry sectors where the potential to exploit EO based services with such new ICT has not yet been explored and demonstrated.
e-Drift is based on a strong network between providers of value-added services utilizing EO data alongside with in-sector providers of the insurance/re-insurance sector as well as other concerned actors in the field, such as World Bank, with the final goal to create new or improved products and solutions for the insurance sector. The project consortium includes leading companies in the EO value adding, and leading actors in the insurance market and concentrates as a pilot study area in South East Asia, more specifically on Myanmar, Laos and Cambodia.
Enhancing the SEADRIF platform with e-Drift
Developing countries, such as many South-East and South Asia countries with middle-low incomes, typically lack financial protection against the impacts of disasters and rely heavily on ex-post measures, such as donor assistance, in order to meet their financing needs. As such, those countries are among the ones that would benefit the most from DRF products.
Based on this demand, in March 2017, at the request of Cambodia, Laos and Myanmar, the World Bank’s Crisis and Disaster Risk Finance team initiated the development of a system to support rapid response financing to flooding events in the region. The project, named South East Asia flood monitoring and risk assessment for regional DRF mechanism led by Deltares (NL) has resulted in an IT platform (SEADRIF) able to estimate the number of people affected by a flood, by a combination of real-time models, EO data and ground observations. The combination of diverse types of input data for a rapid estimate of flood impact is considered highly innovative and responds to the demand from World Bank country clients to be provided with technical and financial tools and means to manage emergencies and save lives.
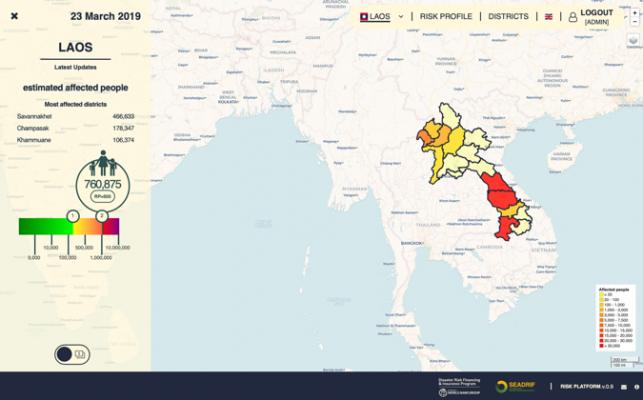
The platform has been running pre-operationally at CIMA Research Foundation since the beginning of 2018 and, during the 2018 flood season in southeast Asia (June-August), it was tested for the first time on actual on-going flood events in NRT. The floods that occurred during the 2018 flood season in Laos were not automatically detected by the platform: floods were caused by a dam break and the hydraulic model was not designed to simulate such event, plus the extremely poor quality of the satellite observations used, mainly based on optical acquisition from MODIS, led to a poor performance of the system.
For the same event, part of the technical team that worked on the SEADRIF platform was triggered by the International Carter on Space and Major Disasters under the coordination of UNOSAT/UNITAR to produce high-resolution flood maps on the area, in support of fast recovering operations. The use of SAR satellite data (Sentinel-1, Radarsat-2, TerraSAR-X) to map the flood extent proved effective to the point that it could have been used to directly estimate the affected population.
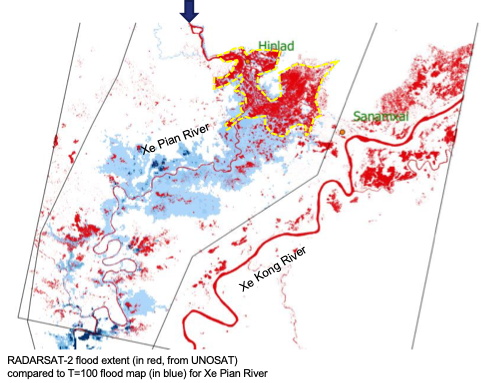
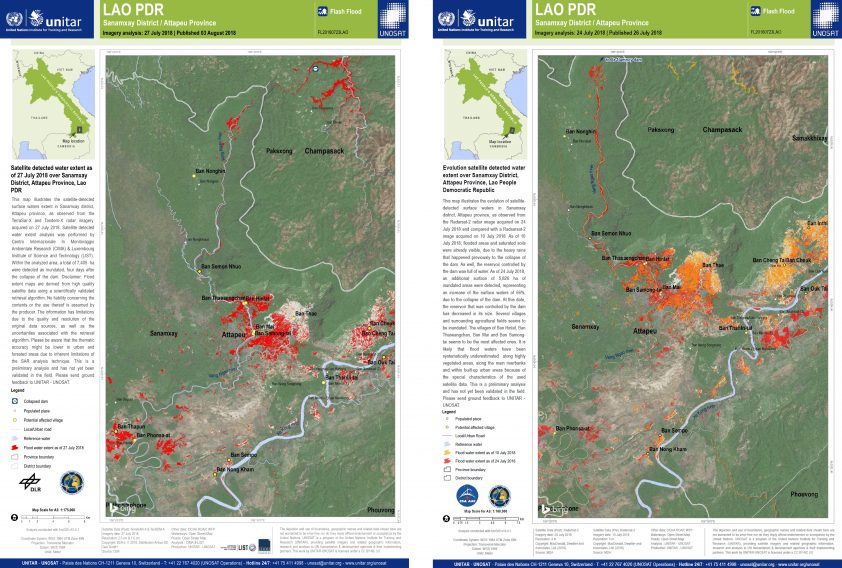
From that experience an upgrade of the satellite component of the SEADRIF platform was planned with the e-Drift project focusing on the rapid evaluation capacity. The two projects are now working together to fully integrate the effectiveness of EO data within the DRF decision-making application. The schematics that follows highlights the e-Drift services that will be soon integrated pre-operationally into the SEADRIF platform.
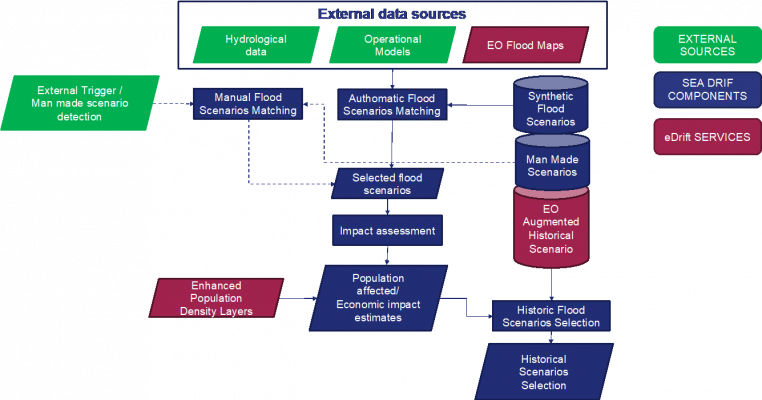
All operational aspects will have to be addressed in order to produce a robust and fully operational monitoring system. The specifications of the e-Drift services are based on the operational requirements of the SEADRIF platform and intended users. Therefore, the aim is to connect in a machine-to-machine configuration the e-Drift services and demonstrate their added value as well as their operational parameters. The demonstration phase is expected to deliver operational results in Q3 2019 and will be completed with an implementation phase shortly after.




 e-DRIFT
e-DRIFT 

